OPCHDA COM/DCOM setup
Background
COM
COM is the standard protocol for communication between objects located on the same computer but which are part of different programs. The server is the object providing services, such as making data available. The client is an application that uses the services provided by the server.
DCOM
DCOM represents an expansion of COM functionality to allow access to objects on remote computers. This protocol allows standardized data exchange between applications from industry, administrative offices and manufacturing. Previously, the applications that accessed the process data were tied to the access protocols of the communication network. The OPC standard software interface allows devices and applications from different manufacturers to be combined in a uniform way.
The OPC client is an application that accesses process data, messages, and archives of an OPC server. Access is through the OPC software interface. An OPC server is a program that provides standard software interface to read or write data. The OPC server is the intermediate layer between the applications for handling process data, the various network protocols and the interfaces for accessing these data. Only devices with operating systems based on Windows COM and DCOM technology can use the OPC software interface for data exchange.
This page gives some hints on how to set up a communication with COM/DCOM to an OPCHDA server. However, in industrial context, it is often the responsibility of the IT team to correctly set the permissions, firewall and Windows configuration.
Windows settings (client)
Client machine settings
Follow these steps to enable COM/DCOM communications from the client. First, open the Component services, and access the Properties of the computer.
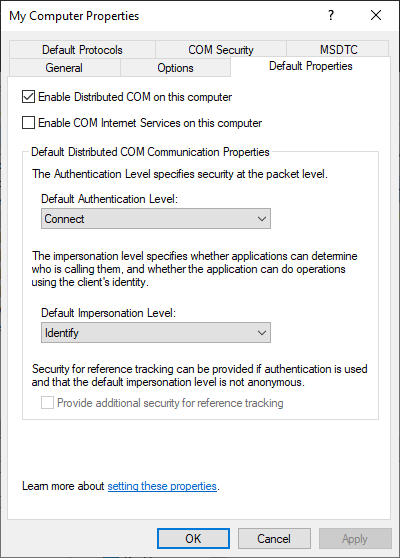
Be sure to enable Distributed COM on this computer.
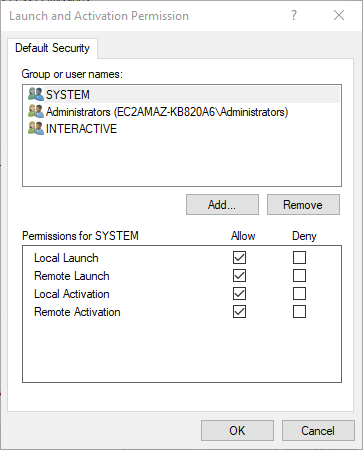
On the COM Security tab, edit default access permissions.
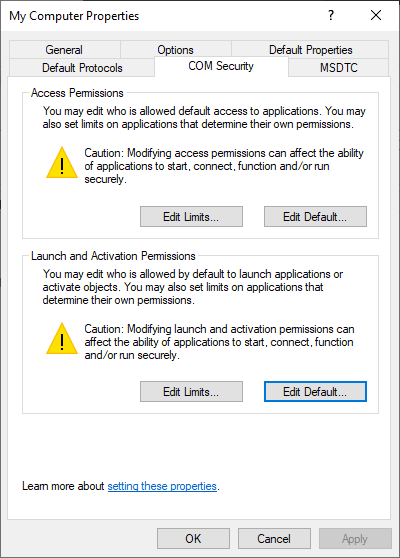
On the Access permissions window, allow the following permissions:
- Local Launch
- Remote Launch
- Local Activation
- Remote Activation
Test communication
DCOM uses port 135 of the HDA server to exchange with the client. To do so, it is interesting to use the tnc command of the Windows Powershell installed as standard. Below, a test that fails (because of the firewall) then a test that succeeds:
tnc 35.180.44.30 -port 135
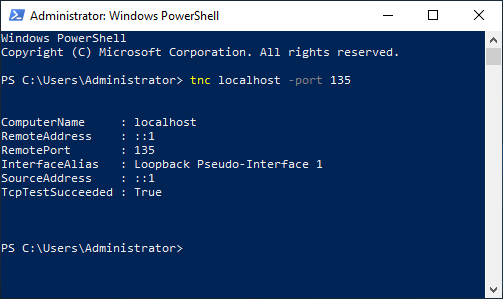
If you have a communication problem, see the firewall configuration section which is probably the source of the problem.
Authentication
An OPCDA client program will communicate with the DA/HDA server with the IP address or hostname of the server followed by the “progId” of the server. It will then have to be identified at the Windows level with a name and a password which are (by default) those of the user who launches the client program. This user must therefore be known on the HDA server as well. You must therefore either:
- Create a user with the same password on the HDA server (assuming it is accessible)
- Be part of the same domain (so the user is accessible from all computers in the domain)
The user must be a member of the Distributed COM Users group
If the program runs through a service (such as OIBus), go to the Service manager window, and right-click on the service. Then click on Launch as user.
Firewall configuration
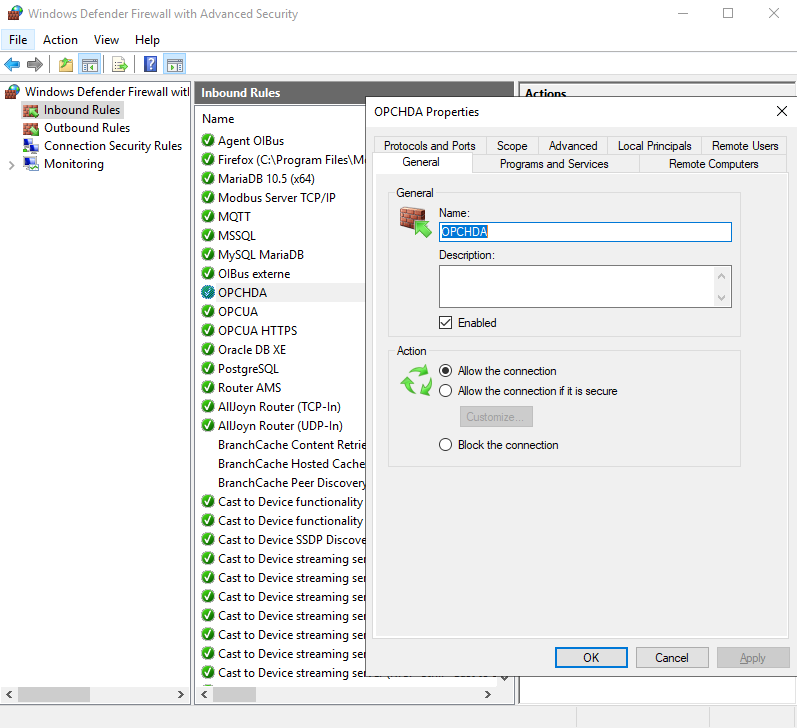
In case of communication issue, the most likely cause is the configuration of a firewall between the two computers and/or at the hosting company in the case of machines on the cloud. On a Windows server, it is possible to configure the firewall by adding a rule on port 135.
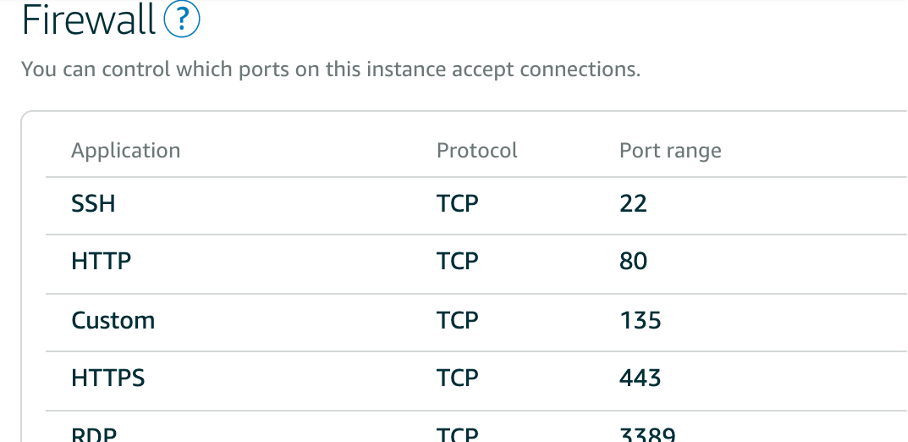
In the case of a server hosted by Lightsail, there is an additional firewall in which a custom rule must be configured for port 135.
OPCEnum tool
The OPC Foundation has provided a tool to allow OPCHDA clients to locate servers on remote nodes, without having
information about those servers in the local registry. This tool is called OPCEnum and is freely distributed by the OPC
Foundation. The PI OPCHDA interface installation installs OPCEnum as well. The primary function of OPCEnum is to inform
or request information from other instances of OPCEnum about existing OPCHDA Servers on the local system. When OPCEnum
is installed, it grants Launch and Access DCOM permission to Everyone and sets the Authentication level to NONE.
This allows access to any user who can log on to the system. The permissions can be changed using dcomcnfg.exe.
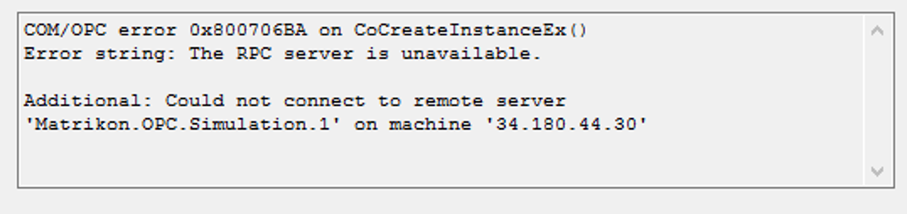
RPC unavailable
If the RPC server is unavailable, try again testing COM/DCOM communication testing COM/DCOM communication and check your firewall.
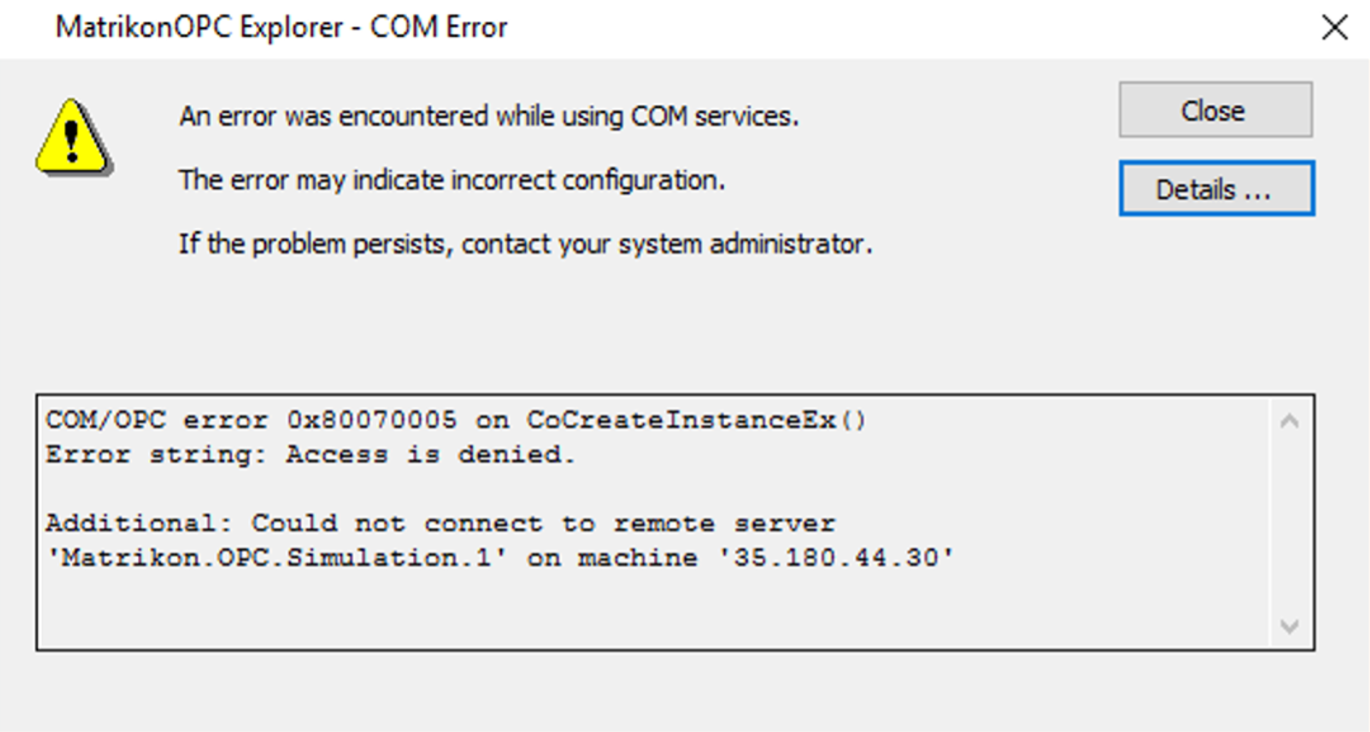
Access denied
Access rights can be diagnosed using the server security log. If the following error happens, check the user and its password created on the HDA server and that the user is in the Distributed COM Users group on the HDA server.
Server settings
Check on the server machine if DCOM is enabled for the OPC Server application by opening the Component Service window.